The OSI model had been around since 1984. In this post, we will talk about why it exists.
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnections) model provides a reference model and a standard guide for how computer applications communicate over a network. It deals with connecting open systems that are open for communication with other systems. The OSI model made it possible for computers made by different manufacturers to communicate over the network. Prior to the OSI model, computers made by different manufacturers were unable to send or receive data across the network. For example, an IBM computer was able to send data only to other IBM computers and it was unable to send or receive data from IBM to Apple or any computer made by any other manufacturer. The model uses 7 layers to help us understand how the data is going through from one computer to another computer.
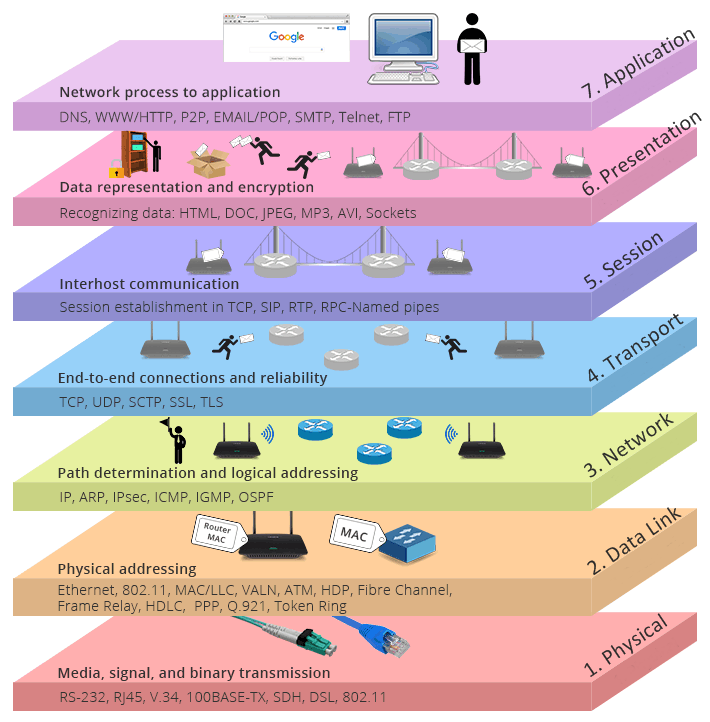
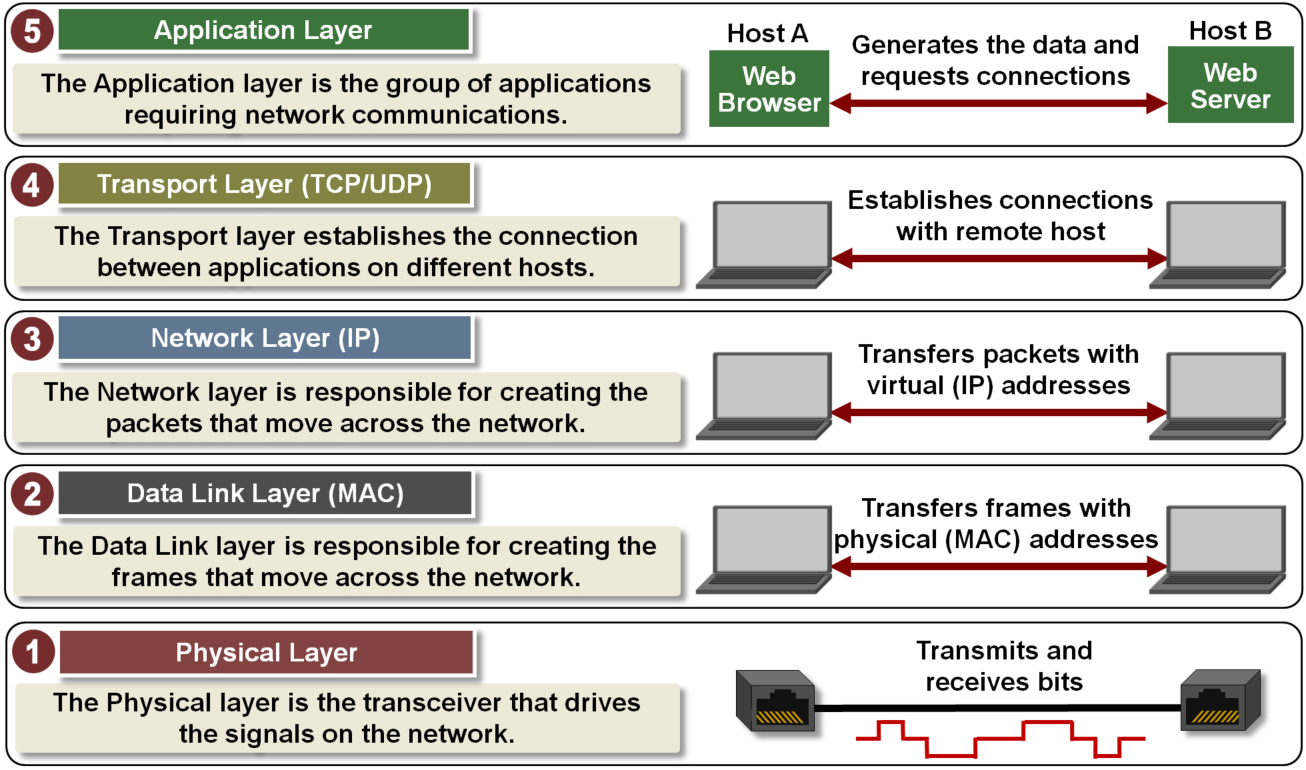
The purpose of OSI Model is to provide safe, secure, and reliable communication between different computers within a network. Today, we can send and receive huge amounts of data safely and reliably at a time because of the OSI model. In fact, everything from gaming, marketing, banking, and the security of the nation is all possible because of the OSI model. The seven layers of OSI model from top to bottom are application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link and physical layer. The layer 7, application layer allows the user to directly interact with an application and it provides the platform for sending and receiving data across the network through emails and world wide web browsers. The layer 6, presentation layer is called a translation layer and it receives data from the application layer and converts those characters and numbers to machine to understand binary format because our computers only understand 0’s and 1’s. The layer 5, session layer deals with the connections. It establishes, manages, and terminates the communications between the nodes and results in connecting the lower layers with the application and the presentation layer. The layer 4, transport layer deals with end to end communication and layer 3, network layer takes care of routing the data between nodes. The layer 2, the data link layer deals with the hardware and as well as software and the last layer. Lastly, the OSI model layer 1, physical layer deals with bits at the hardware level.
I feel that the OSI model’s biggest contribution is that it provides abstraction between services, interfaces, and protocols by separating them into different layers where each layer provides base foundation to the layer above it. A layer service tells what the later does, not how other processes can access it. A layer interface tells processes how to access it. A layer can use any protocols it wants to as long as it gets the job done and changing protocols in the layer will not affect software in higher layers.
Finally, the OSI model plays a great role in providing network security. The data link layer takes care of reliable transmission of the data by error control where the errors are detected and corrected. The network layer of the OSI model ensures confidentiality by sending the data to the correct destination in a secured way through internet protocol (IP) addresses.
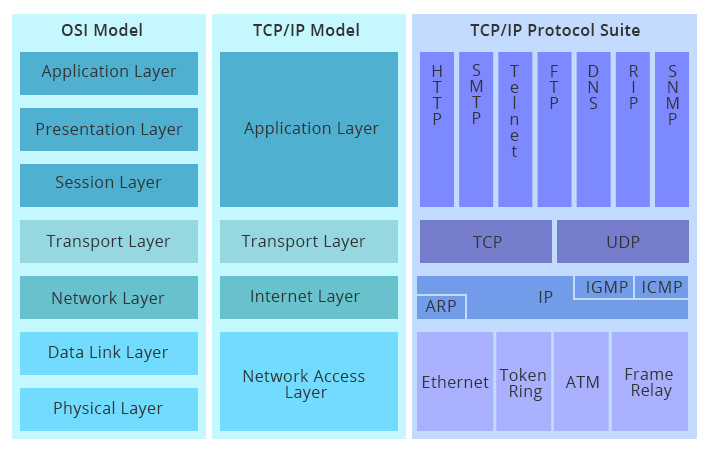
Important information about the Open Source Interconnect (OSI) model and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/Internet Protocol (IP).
TCP/IP, OSI Models
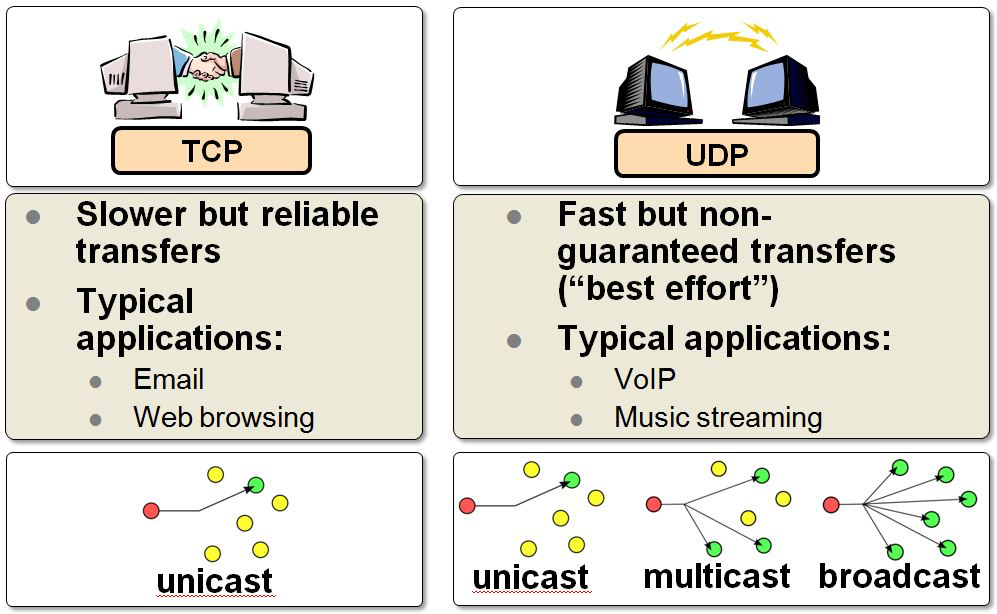
TCP vs UDP
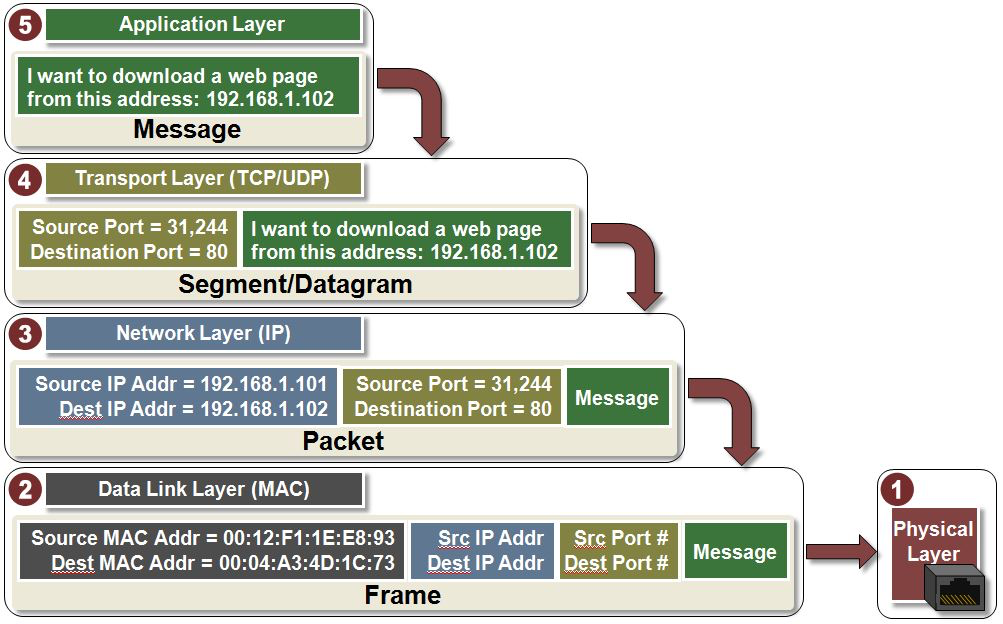
Some applications require reliable ordered delivery of packets. The TCP protocol provides this capability. It uses error detection, retransmissions and acknowledgements. This protocol cares about your data.
 ,
,
